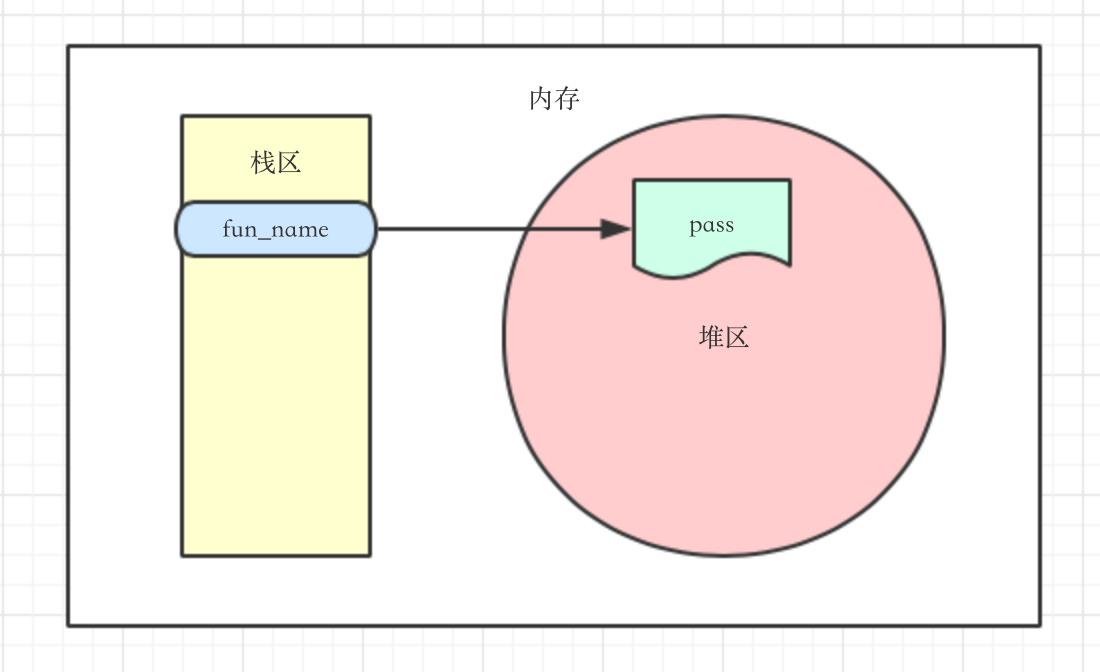
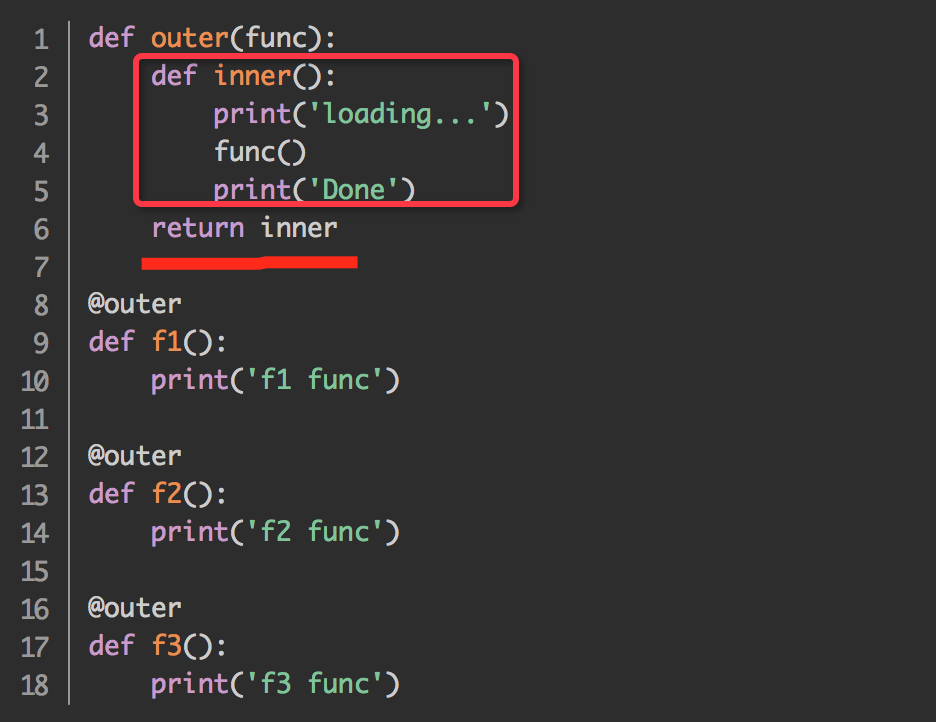
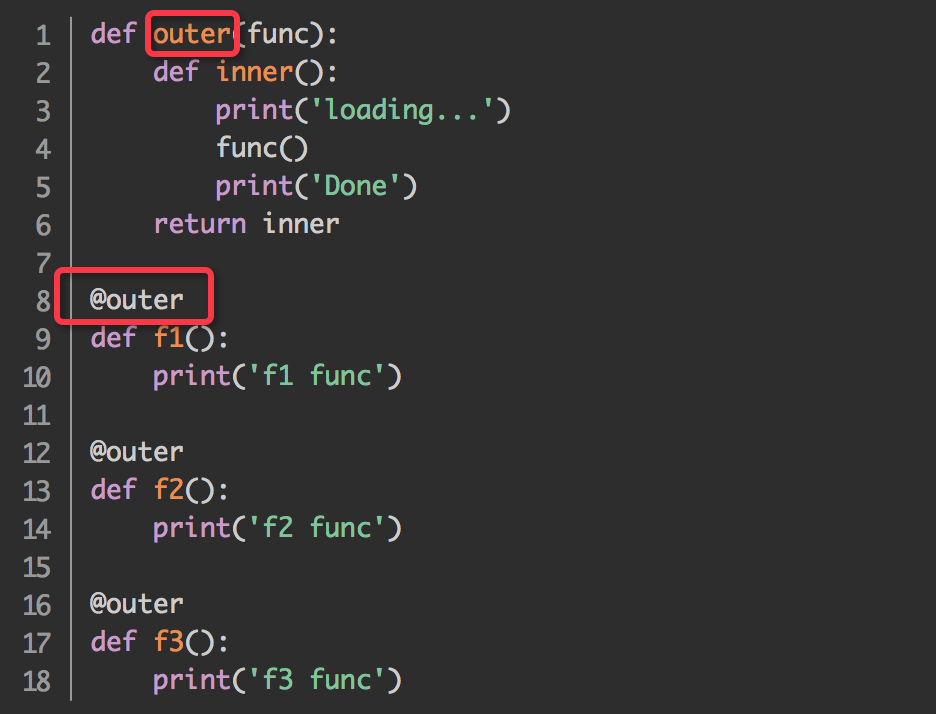
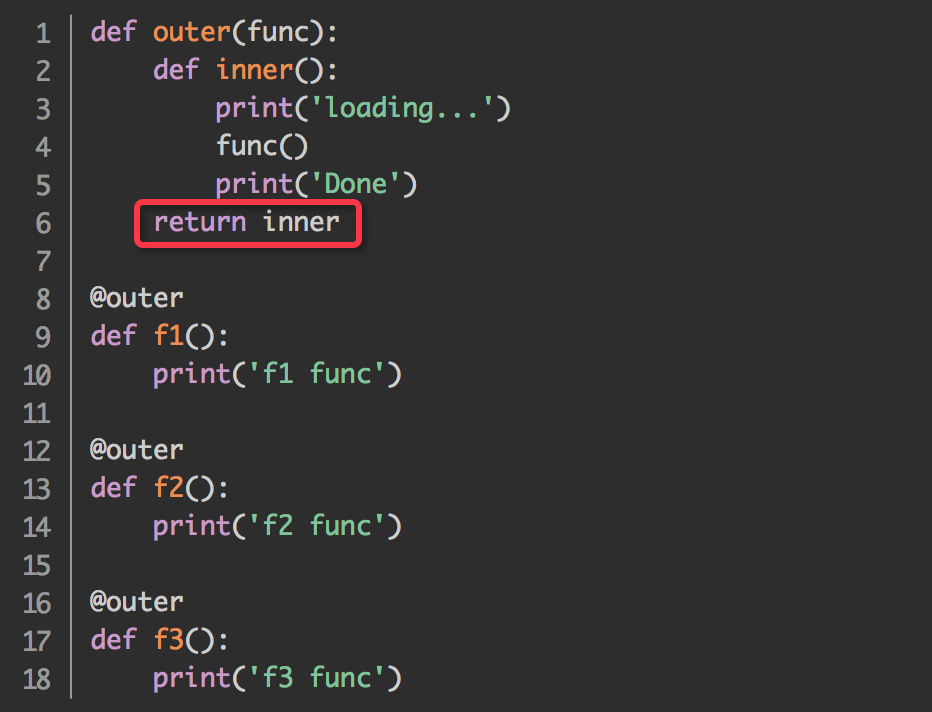
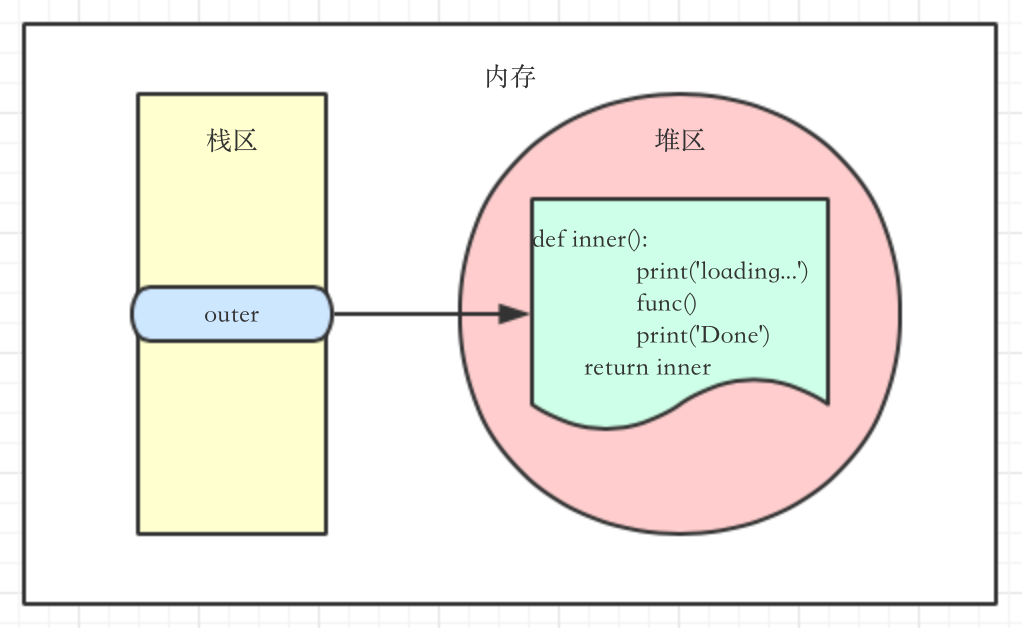
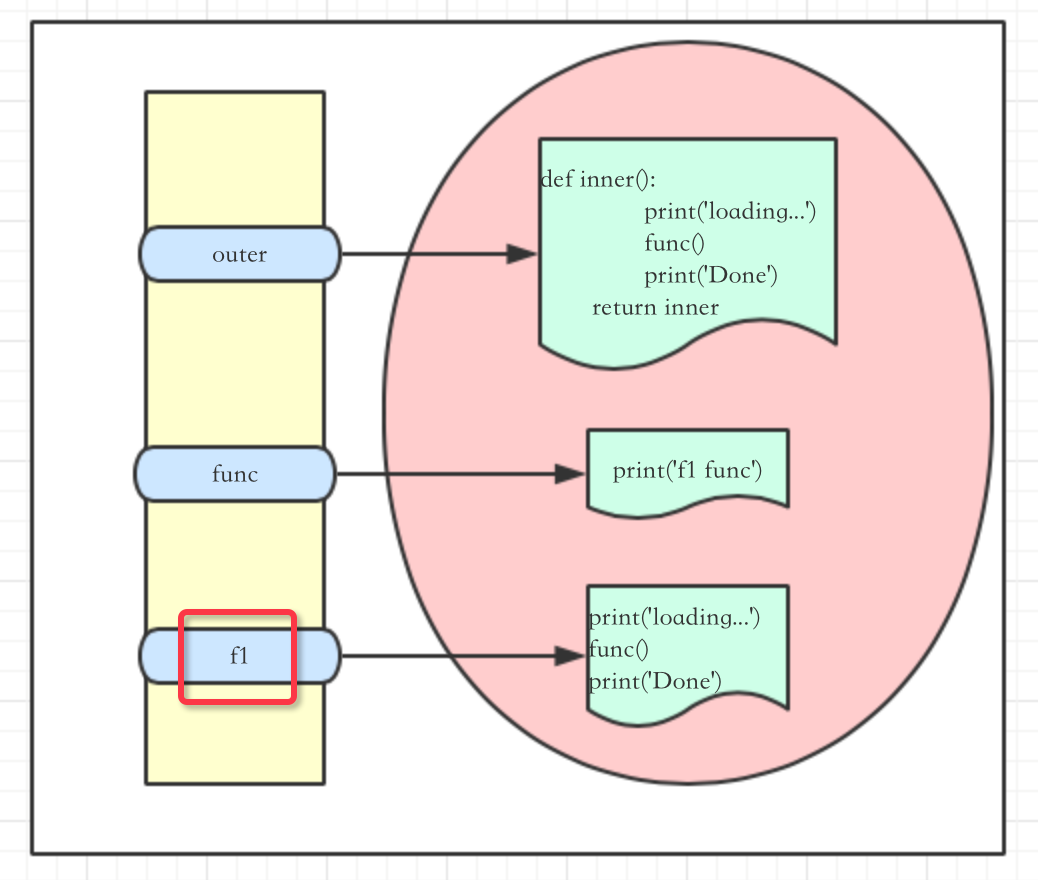
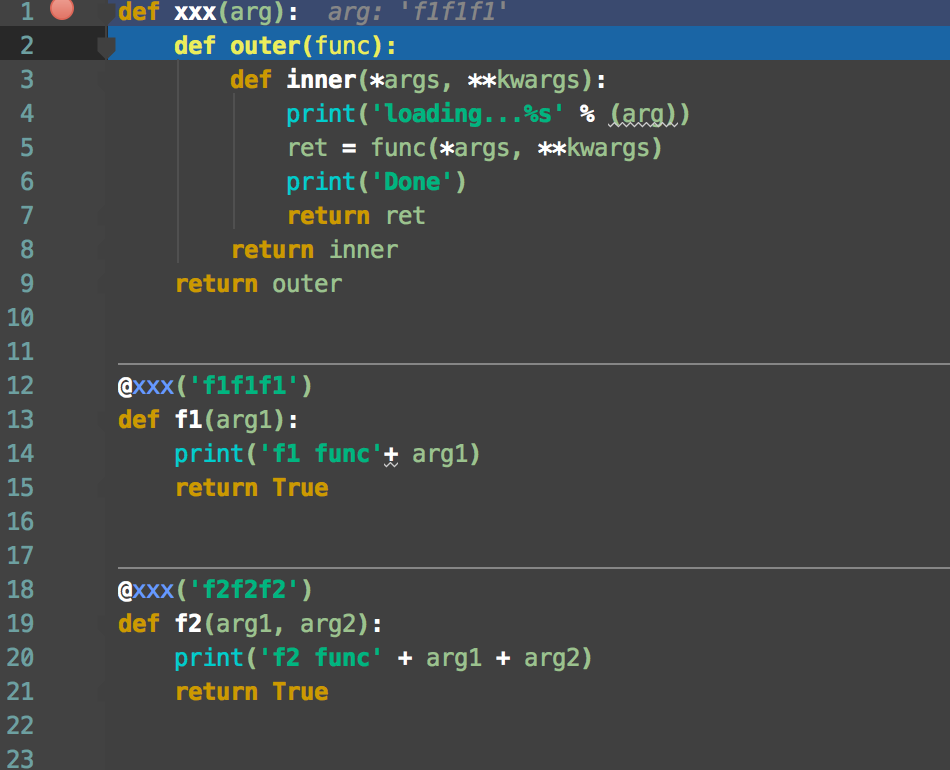
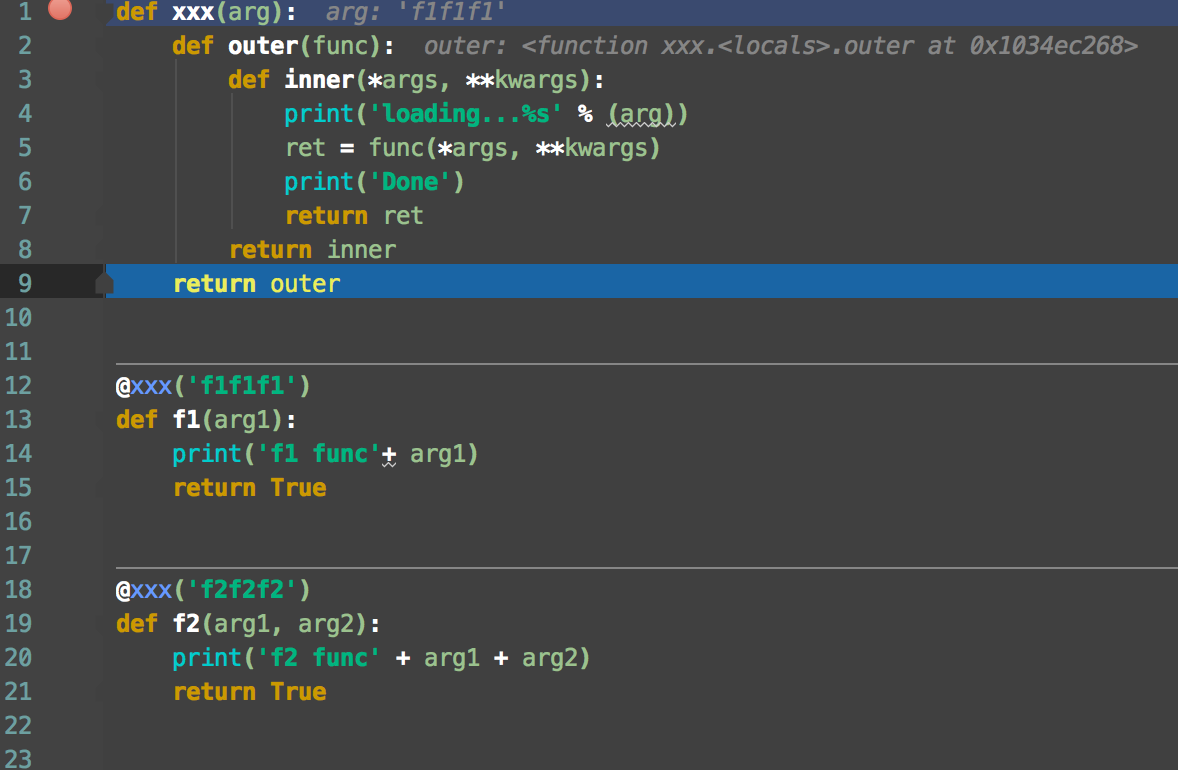
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
| class Logger(Filterer):
"""
Instances of the Logger class represent a single logging channel. A
"logging channel" indicates an area of an application. Exactly how an
"area" is defined is up to the application developer. Since an
application can have any number of areas, logging channels are identified
by a unique string. Application areas can be nested (e.g. an area
of "input processing" might include sub-areas "read CSV files", "read
XLS files" and "read Gnumeric files"). To cater for this natural nesting,
channel names are organized into a namespace hierarchy where levels are
separated by periods, much like the Java or Python package namespace. So
in the instance given above, channel names might be "input" for the upper
level, and "input.csv", "input.xls" and "input.gnu" for the sub-levels.
There is no arbitrary limit to the depth of nesting.
"""
def __init__(self, name, level=NOTSET):
"""
Initialize the logger with a name and an optional level.
"""
Filterer.__init__(self)
self.name = name
self.level = _checkLevel(level)
self.parent = None
self.propagate = True
self.handlers = []
self.disabled = False
def setLevel(self, level):
"""
Set the logging level of this logger. level must be an int or a str.
"""
self.level = _checkLevel(level)
def debug(self, msg, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Log 'msg % args' with severity 'DEBUG'.
To pass exception information, use the keyword argument exc_info with
a true value, e.g.
logger.debug("Houston, we have a %s", "thorny problem", exc_info=1)
"""
if self.isEnabledFor(DEBUG):
self._log(DEBUG, msg, args, **kwargs)
def info(self, msg, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Log 'msg % args' with severity 'INFO'.
To pass exception information, use the keyword argument exc_info with
a true value, e.g.
logger.info("Houston, we have a %s", "interesting problem", exc_info=1)
"""
if self.isEnabledFor(INFO):
self._log(INFO, msg, args, **kwargs)
def warning(self, msg, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Log 'msg % args' with severity 'WARNING'.
To pass exception information, use the keyword argument exc_info with
a true value, e.g.
logger.warning("Houston, we have a %s", "bit of a problem", exc_info=1)
"""
if self.isEnabledFor(WARNING):
self._log(WARNING, msg, args, **kwargs)
def warn(self, msg, *args, **kwargs):
warnings.warn("The 'warn' method is deprecated, "
"use 'warning' instead", DeprecationWarning, 2)
self.warning(msg, *args, **kwargs)
def error(self, msg, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Log 'msg % args' with severity 'ERROR'.
To pass exception information, use the keyword argument exc_info with
a true value, e.g.
logger.error("Houston, we have a %s", "major problem", exc_info=1)
"""
if self.isEnabledFor(ERROR):
self._log(ERROR, msg, args, **kwargs)
def exception(self, msg, *args, exc_info=True, **kwargs):
"""
Convenience method for logging an ERROR with exception information.
"""
self.error(msg, *args, exc_info=exc_info, **kwargs)
def critical(self, msg, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Log 'msg % args' with severity 'CRITICAL'.
To pass exception information, use the keyword argument exc_info with
a true value, e.g.
logger.critical("Houston, we have a %s", "major disaster", exc_info=1)
"""
if self.isEnabledFor(CRITICAL):
self._log(CRITICAL, msg, args, **kwargs)
fatal = critical
def log(self, level, msg, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Log 'msg % args' with the integer severity 'level'.
To pass exception information, use the keyword argument exc_info with
a true value, e.g.
logger.log(level, "We have a %s", "mysterious problem", exc_info=1)
"""
if not isinstance(level, int):
if raiseExceptions:
raise TypeError("level must be an integer")
else:
return
if self.isEnabledFor(level):
self._log(level, msg, args, **kwargs)
def findCaller(self, stack_info=False):
"""
Find the stack frame of the caller so that we can note the source
file name, line number and function name.
"""
f = currentframe()
if f is not None:
f = f.f_back
rv = "(unknown file)", 0, "(unknown function)", None
while hasattr(f, "f_code"):
co = f.f_code
filename = os.path.normcase(co.co_filename)
if filename == _srcfile:
f = f.f_back
continue
sinfo = None
if stack_info:
sio = io.StringIO()
sio.write('Stack (most recent call last):\n')
traceback.print_stack(f, file=sio)
sinfo = sio.getvalue()
if sinfo[-1] == '\n':
sinfo = sinfo[:-1]
sio.close()
rv = (co.co_filename, f.f_lineno, co.co_name, sinfo)
break
return rv
def makeRecord(self, name, level, fn, lno, msg, args, exc_info,
func=None, extra=None, sinfo=None):
"""
A factory method which can be overridden in subclasses to create
specialized LogRecords.
"""
rv = _logRecordFactory(name, level, fn, lno, msg, args, exc_info, func,
sinfo)
if extra is not None:
for key in extra:
if (key in ["message", "asctime"]) or (key in rv.__dict__):
raise KeyError("Attempt to overwrite %r in LogRecord" % key)
rv.__dict__[key] = extra[key]
return rv
def _log(self, level, msg, args, exc_info=None, extra=None, stack_info=False):
"""
Low-level logging routine which creates a LogRecord and then calls
all the handlers of this logger to handle the record.
"""
sinfo = None
if _srcfile:
try:
fn, lno, func, sinfo = self.findCaller(stack_info)
except ValueError:
fn, lno, func = "(unknown file)", 0, "(unknown function)"
else:
fn, lno, func = "(unknown file)", 0, "(unknown function)"
if exc_info:
if isinstance(exc_info, BaseException):
exc_info = (type(exc_info), exc_info, exc_info.__traceback__)
elif not isinstance(exc_info, tuple):
exc_info = sys.exc_info()
record = self.makeRecord(self.name, level, fn, lno, msg, args,
exc_info, func, extra, sinfo)
self.handle(record)
def handle(self, record):
"""
Call the handlers for the specified record.
This method is used for unpickled records received from a socket, as
well as those created locally. Logger-level filtering is applied.
"""
if (not self.disabled) and self.filter(record):
self.callHandlers(record)
def addHandler(self, hdlr):
"""
Add the specified handler to this logger.
"""
_acquireLock()
try:
if not (hdlr in self.handlers):
self.handlers.append(hdlr)
finally:
_releaseLock()
def removeHandler(self, hdlr):
"""
Remove the specified handler from this logger.
"""
_acquireLock()
try:
if hdlr in self.handlers:
self.handlers.remove(hdlr)
finally:
_releaseLock()
def hasHandlers(self):
"""
See if this logger has any handlers configured.
Loop through all handlers for this logger and its parents in the
logger hierarchy. Return True if a handler was found, else False.
Stop searching up the hierarchy whenever a logger with the "propagate"
attribute set to zero is found - that will be the last logger which
is checked for the existence of handlers.
"""
c = self
rv = False
while c:
if c.handlers:
rv = True
break
if not c.propagate:
break
else:
c = c.parent
return rv
def callHandlers(self, record):
"""
Pass a record to all relevant handlers.
Loop through all handlers for this logger and its parents in the
logger hierarchy. If no handler was found, output a one-off error
message to sys.stderr. Stop searching up the hierarchy whenever a
logger with the "propagate" attribute set to zero is found - that
will be the last logger whose handlers are called.
"""
c = self
found = 0
while c:
for hdlr in c.handlers:
found = found + 1
if record.levelno >= hdlr.level:
hdlr.handle(record)
if not c.propagate:
c = None
else:
c = c.parent
if (found == 0):
if lastResort:
if record.levelno >= lastResort.level:
lastResort.handle(record)
elif raiseExceptions and not self.manager.emittedNoHandlerWarning:
sys.stderr.write("No handlers could be found for logger"
" \"%s\"\n" % self.name)
self.manager.emittedNoHandlerWarning = True
def getEffectiveLevel(self):
"""
Get the effective level for this logger.
Loop through this logger and its parents in the logger hierarchy,
looking for a non-zero logging level. Return the first one found.
"""
logger = self
while logger:
if logger.level:
return logger.level
logger = logger.parent
return NOTSET
def isEnabledFor(self, level):
"""
Is this logger enabled for level 'level'?
"""
if self.manager.disable >= level:
return False
return level >= self.getEffectiveLevel()
def getChild(self, suffix):
"""
Get a logger which is a descendant to this one.
This is a convenience method, such that
logging.getLogger('abc').getChild('def.ghi')
is the same as
logging.getLogger('abc.def.ghi')
It's useful, for example, when the parent logger is named using
__name__ rather than a literal string.
"""
if self.root is not self:
suffix = '.'.join((self.name, suffix))
return self.manager.getLogger(suffix)
|